What is Industry 4.0?
Industry 4.0, also known as the Fourth Industrial Revolution, refers to the ongoing transformation of traditional manufacturing and industrial processes through the integration of digital technologies. It represents a paradigm shift in the way products are designed, produced, and distributed, driven by advancements in areas such as automation, artificial intelligence, big data analytics, the Internet of Things (IoT), and cloud computing.
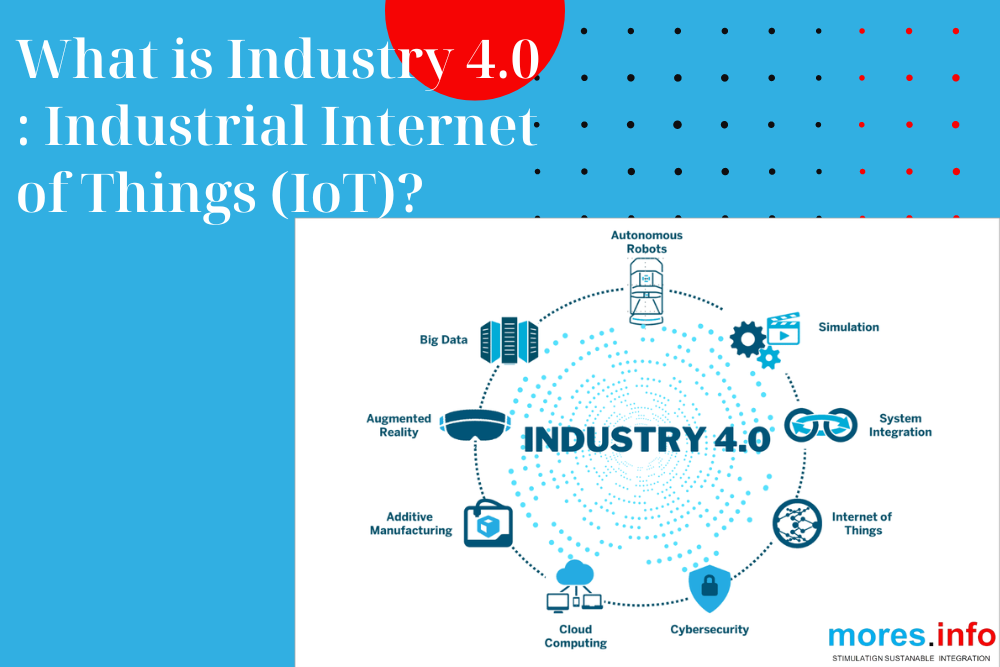
Key characteristics of Industry 4.0 include
- Interconnectivity: Machines, devices, sensors, and other components are interconnected through IoT technology, enabling seamless communication and data exchange across the entire manufacturing ecosystem.
- Data Analytics: The collection and analysis of vast amounts of data from various sources provide insights that drive informed decision-making, optimize processes, and improve efficiency and productivity.
- Automation and Robotics: Automation technologies, including robotics and autonomous systems, are increasingly used to perform repetitive tasks, streamline production processes, and enhance precision and quality.
- Cyber-Physical Systems: The integration of physical systems with digital technologies enables real-time monitoring, control, and optimization of manufacturing operations, leading to greater flexibility and responsiveness.
- Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing): Additive manufacturing technologies, such as 3D printing, enable the rapid prototyping and production of complex components with reduced material waste and shorter lead times.
- Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR): AR and VR technologies are utilized for training, maintenance, and visualization purposes, allowing workers to interact with digital information overlaid onto the physical environment.
- Supply Chain Integration: Industry 4.0 emphasizes the integration of supply chains through digital platforms, enabling seamless coordination and collaboration among suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors.
- Customization and Personalization: The digitization of manufacturing processes enables greater customization and personalization of products to meet individual customer needs and preferences.
Industry 4.0 represents a transformative shift in the way industries operate, offering opportunities for increased efficiency, agility, innovation, and competitiveness. It has the potential to revolutionize traditional manufacturing models, empower businesses to adapt to changing market demands, and drive economic growth and prosperity in the digital age.
Internet of Things
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to a network of interconnected devices, sensors, machines, and objects that communicate with each other over the internet or other communication networks. These “smart” devices are embedded with sensors, software, and other technologies that enable them to collect and exchange data, as well as perform specific functions or tasks.
Key characteristics of the Internet of Things
- Interconnectivity: IoT devices are connected to each other and to the internet, allowing for seamless communication and data exchange. This interconnected network enables devices to work together, share information, and collaborate on tasks.
- Sensing and Data Collection: IoT devices are equipped with sensors that gather data from the surrounding environment, such as temperature, humidity, light, motion, and more. This data is then transmitted to other devices or systems for analysis and action.
- Remote Monitoring and Control: IoT enables remote monitoring and control of devices and systems from anywhere with an internet connection. This capability allows users to monitor and manage their devices in real-time, regardless of their location.
- Automation and Efficiency: IoT technology can automate various processes and tasks, leading to increased efficiency, productivity, and cost savings. By connecting devices and enabling them to communicate and coordinate actions, IoT streamlines workflows and reduces the need for manual intervention.
- Improved Decision-Making: The data collected by IoT devices can provide valuable insights and analytics that inform decision-making and drive business outcomes. By analyzing data in real-time, organizations can identify trends, patterns, and anomalies, enabling them to make more informed and timely decisions.
- Enhanced Connectivity: IoT facilitates connectivity across different devices, systems, and platforms, enabling interoperability and integration. This connectivity enables seamless communication and collaboration between devices, as well as interoperability with existing infrastructure and technologies.
- Applications across Industries: IoT technology has applications across various industries, including healthcare, manufacturing, transportation, agriculture, smart cities, and more. From wearable health trackers to smart home devices to industrial automation systems, IoT is transforming how industries operate and deliver value to customers.
Overall, the Internet of Things represents a paradigm shift in how devices and systems interact and collaborate, offering numerous opportunities for innovation, efficiency, and improved experiences across industries and sectors.
How Did We Get to Industry 4.0: Evolution of Industry from 1.0 to Present Day
The First Industrial Revolution
The First Industrial Revolution, often referred to as the Industrial Revolution, marked a significant turning point in human history, characterized by the transition from agrarian and handicraft-based economies to industrialized societies powered by machinery and technology. This transformative period began in the late 18th century and continued into the early 19th century, primarily in Europe and later spreading to other parts of the world.
Key features of the First Industrial Revolution include:
- Mechanization of Production
- Invention of New Technologies
- Expansion of Transportation Networks
- Urbanization and Migration
- Rise of Capitalism and Industrial Capital
- Social and Economic Transformations
- Impact on Global Trade and Imperialism
The Second Industrial Revolution
The Second Industrial Revolution, also known as the Technological Revolution, occurred during the late 19th and early 20th centuries and was characterized by significant advancements in technology, industry, and transportation. This era marked a profound transformation in manufacturing processes, economic structures, and societal norms, paving the way for modern industrial society.
Key developments and innovations of the Second Industrial Revolution include:
- Expansion of Industrialization
- Technological Advancements
- Mass Production and Assembly Lines
- Expansion of Transportation Networks
- Rise of Industrial Giants
- Urbanization and Migration
- Impact on Society and Culture
The Third Industrial Revolution
The Third Industrial Revolution, also known as the Digital Revolution or the Information Age, emerged in the late 20th century and continues to shape the contemporary world. This era is characterized by the widespread adoption of digital technologies, automation, and the internet, leading to profound changes in the way people live, work, and communicate.
Key developments and innovations of the Third Industrial Revolution include:
- Information Technology
- Internet and World Wide Web
- Digitalization of Industries
- E-commerce and Digital Economy
- Mobile and Personal Computing
- Big Data and Analytics
- Social Media and Networking
- Cyber security and Privacy Concerns
The Fourth Industrial Revolution or Industry 4.0
The Fourth Industrial Revolution, also known as Industry 4.0, represents the ongoing transformation of traditional manufacturing and industrial processes through the integration of digital technologies. This era builds upon the advancements of the previous industrial revolutions and is characterized by the convergence of physical, digital, and biological systems.
Key features of the Fourth Industrial Revolution, or Industry 4.0, include:
- Internet of Things (IoT): The proliferation of connected devices, sensors, and machines enables real-time data collection, analysis, and communication across the entire manufacturing ecosystem. This interconnected network of “smart” devices facilitates automation, predictive maintenance, and optimized production processes.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning: AI technologies enable machines and systems to learn from data, recognize patterns, and make autonomous decisions. Machine learning algorithms drive advancements in areas such as predictive analytics, quality control, and robotics, enhancing efficiency and productivity in manufacturing.
- Big Data Analytics: The abundance of data generated by IoT devices, sensors, and other sources is leveraged through big data analytics to derive actionable insights and inform decision-making. Advanced analytics techniques enable manufacturers to optimize processes, identify opportunities for improvement, and anticipate market trends.
- Advanced Robotics: Robotics technology is increasingly integrated into manufacturing operations to automate repetitive tasks, enhance precision, and improve safety. Collaborative robots (cobots) work alongside human workers, increasing flexibility and agility in production environments.
- Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing): Additive manufacturing technologies enable the rapid prototyping and production of complex components with reduced material waste and shorter lead times. 3D printing offers new possibilities for customization, design optimization, and on-demand manufacturing.
- Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR): AR and VR technologies are used for training, maintenance, and visualization purposes in manufacturing. AR overlays digital information onto the physical environment, providing workers with real-time instructions and guidance, while VR creates immersive simulations for training and design purposes.
- Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS): CPS integrate physical components with digital technologies to monitor and control physical processes in real-time. These systems enable autonomous operation, adaptive manufacturing, and the creation of “smart” factories capable of self-optimization and self-correction.
- Digital Twins: Digital twins are virtual representations of physical assets, processes, or systems that enable real-time monitoring, analysis, and optimization. By simulating the behavior of physical assets in a digital environment, manufacturers can identify opportunities for improvement and optimize performance.

Hi, this is a comment.
To get started with moderating, editing, and deleting comments, please visit the Comments screen in the dashboard.
Commenter avatars come from Gravatar.